|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
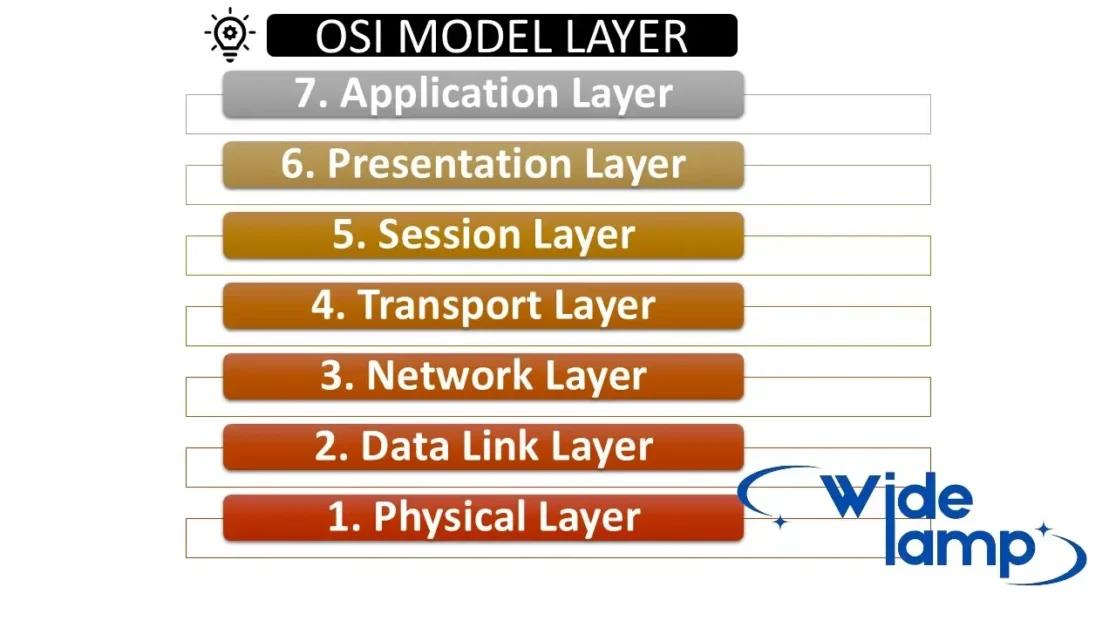
Let’s dive into what is OSI Model or layer. OSI Model/Layer is the most important part of cybersecurity, OSI understands Open System Intercommunication. The OSI model has 7 layers model every layer defines a section and every section works one by one. If any layer is missing in the OSI Model no one works so every layer of the OSI model is important.
OSI model has a Physical layer, Data link layer, Network layer, Transport layer, Session layer, Presentation layer, and Application layer. you can understand the OSI Model as an example: you are a human and you have a body that works with your spirit (Atma) if your body is empty without any spirit you don’t do anything. if you have spirit then you work. all layers are working together
What Is OSI Model?
Let’s discuss every single OSI layer……..
OSI Model PhysicalData LinkNetworkTransportSessionPresentationApplication Layer
Layer 1 – Physical Layer Transmit row bit across the physical layer
This layer works in the initial stage because without any physical layer, you don’t run any system, physical means hardware.
Function: This is the lowest layer of the OSI model, responsible for the physical connection between devices. It deals with the transmission and reception of raw binary data over a physical medium, such as cables, radio frequencies, or fiber optics.
Examples: Ethernet cables, Wi-Fi signals, and network interface cards (NICs) operate at this layer.
Model: Imagine the physical layer as the road that vehicles (data) travel on. The type of road (e.g., highway, dirt road) affects how fast and efficiently vehicles can move.
Layer 2 – Data Link Layer Defines the format of data across the network
Function: The data link layer ensures that data is transferred error-free from one node to another over the physical layer. It packages data into frames and handles error detection, correction, and flow control.
Examples: MAC addresses, Ethernet, and switches operate at this layer.
Model: Consider this layer as the rules and signs on the road (e.g., traffic lights, lane markers) that help vehicles (data frames) move smoothly and avoid collisions.
Layer 3 – Network Layer Choose the physical path the data will define
Function: The network layer is responsible for determining the best physical path for data to reach its destination. It handles logical addressing, routing, and packet forwarding.
Examples: IP addresses, routers, and IP protocols work at this layer.
Model: This layer acts like a GPS that decides the best route for vehicles (data packets) to reach their destination, navigating through various roads (networks).
Layer 4 – Transport Layer Transmit data using transmission protocol (UDP, TCP, etc.)
Function: The transport layer ensures reliable data transfer between devices by providing error recovery and flow control. It segments data and reassembles it at the destination.
Examples: TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are key protocols at this layer.
Model: Think of this layer as a delivery service that ensures packages (data segments) are delivered intact and in the correct order. It can resend a package if it gets lost or damaged.
Read More: All About Red Hat
Layer 5 – Session Layer Maintain connections and it’s responsible for controlling port and sessions
Function: The session layer manages sessions or connections between applications. It establishes, maintains, and terminates communication sessions.
Examples: Session management protocols like PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) and NetBIOS operate here.
Model: This layer is like a phone operator that establishes and maintains a call between two parties. It ensures that the conversation (session) continues smoothly and can reconnect if the line drops.
Layer 6 – Presentation Layer Maintain connections and it’s responsible for controlling port and sessions
Function: The presentation layer translates data between the application layer and the network. It handles data encryption, compression, and formatting.
Examples: SSL/TLS encryption, JPEG, and ASCII are handled at this layer.
Model: Imagine this layer as a translator who converts the language (data format) into something the recipient can understand and, if needed, encrypts it for security.
Layer 7 – Application Layer Computer Interface layer, where you can use computer applications and access the network services
Function: The topmost layer, the application layer, interacts directly with end-user software. It provides network services to applications and facilitates user interaction with the network.
Examples: HTTP, FTP, email protocols (SMTP), and DNS operate at this layer.
Model: This layer is like the user interface of an application, where you directly interact with the system. It’s the service (e.g., email, web browsing) that you use to send or receive data

Q & A – Section
Questions which are very helpful for everyone and clear some doubt…
-
What is the OSI Model?

The OSI Model, which stands for Open Systems Interconnection Model, is a framework used to understand how different parts of a network communicate. It has 7 layers, each performing a specific function to help data travel across a network.
-
Why is the OSI Model important?

The OSI Model is crucial because it breaks down the complex process of networking into manageable layers. Each layer has a specific role, and if any layer is missing, the network won’t work properly.
-
What are the 7 layers of the OSI Model?

The 7 layers are:
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer
Presentation Layer
Application Layer -
What does the Physical Layer do?

The Physical Layer is responsible for transmitting raw bits of data over physical media like cables or radio signals. It’s the first step in the network communication process.
-
What is the role of the Data Link Layer?

The Data Link Layer ensures that data is sent error-free from one device to another. It packages the data into frames and manages error detection and correction.
-
What does the Network Layer do?

The Network Layer determines the best path for data to travel from the source to the destination. It handles logical addressing and routing of data packets.
-
How does the Transport Layer work?

The Transport Layer makes sure data is transferred reliably between devices. It breaks data into smaller segments, reassembles it at the destination, and manages error recovery.
-
What is the function of the Session Layer?

The Session Layer manages connections between applications. It sets up, maintains, and ends communication sessions between devices.
-
What does the Presentation Layer handle?

The Presentation Layer translates data between the application layer and the network. It takes care of data encryption, compression, and formatting.
-
What is the role of the Application Layer?

The Application Layer is the top layer where users interact with network services. It provides network services to applications and allows users to access the network.
-
Can you give a simple analogy for the OSI layers?

Think of the OSI layers like a human body. Each layer has a specific role, similar to how different body parts have specific functions. Just as a body needs all parts to work together, all OSI layers must work together for proper network communication.
Form any question suggestion and recommendation please contact on contact@widelamp.com